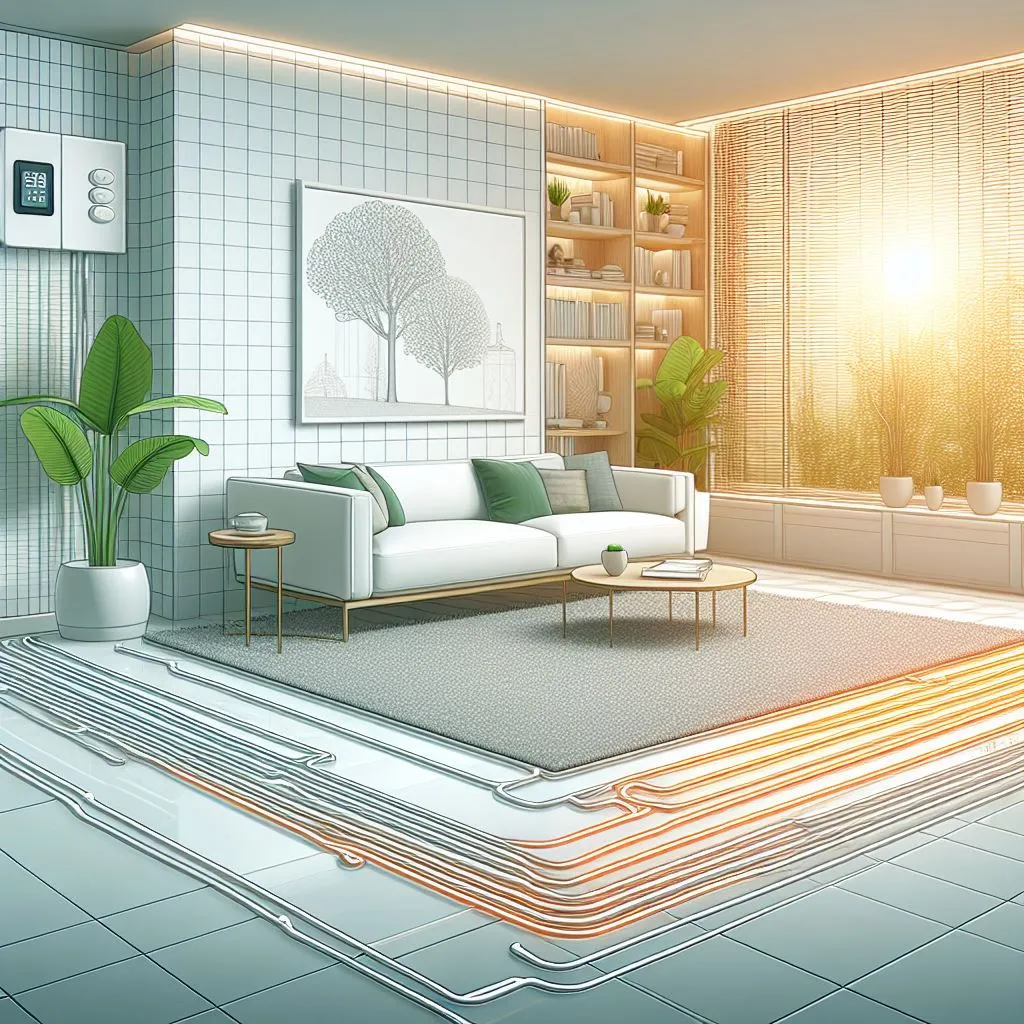
Radiant floor heating is an innovative and efficient method of heating spaces by delivering warmth directly to the floor surface. Unlike traditional forced-air systems that rely on circulating hot air, radiant heating systems transfer heat through the floor, providing a comfortable and even distribution of warmth. Visit our SVR Trace to see the best related products.
The primary components of a Radiant floor heating system include a heat source, typically a boiler or water heater, and a network of pipes or electric heating elements embedded in the floor. Water-based systems circulate warm water through the pipes, while electric systems use heating cables or mats. As the floor warms up, it radiates heat upward, creating a cozy and consistent temperature throughout the room. Check our shop for the best heating cables and order now!
One of the key advantages of Radiant floor heating is its energy efficiency. The heat transfer is more direct, reducing heat loss and allowing for lower operating temperatures compared to traditional systems. This not only saves energy but also enhances indoor air quality by minimizing the circulation of dust and allergens often associated with forced-air systems. Contact us for more data!
Radiant floor heating is versatile and compatible with various flooring materials, including tile, stone, wood, and carpet. Its discreet installation beneath the floor eliminates the need for bulky radiators or vents, contributing to a clean and aesthetically pleasing interior design.
In conclusion, Radiant floor heating offers a modern and efficient solution for maintaining a comfortable indoor environment. Whether in residential or commercial settings, this technology provides a silent, cost-effective, and visually appealing alternative to conventional heating systems.
Visit our blog page for the newest content about industrial products and household products in the field of the radiant floor heating cables!
- How Radiant Floor Heating Works?
- What are the Advantages of Radiant Floor Heating?
- What are the Types of Radiant Floor Heating Systems?
- What are the Installation Process and Considerations of radiant floor heating?
- What are the Costs and Return on Investment of radiant floor heating?
- What are the Maintenance Tips for Radiant Heating Systems?
- What is the Environmental Impact of Radiant Heating?
- What are the Popular Applications of Radiant Floor Heating?
- What are the Challenges and Considerations of radiant floor heating?
These are the questions that will be answered in this article. So lets continue!
Table of contents
- Introduction to Radiant Floor Heating
- How Radiant Floor Heating Works
- Advantages of Radiant Floor Heating
- Types of Radiant Floor Heating Systems
- Installation Process and Considerations
- Costs and Return on Investment
- Maintenance Tips for Radiant Heating Systems
- Environmental Impact of Radiant Heating
- Popular Applications of Radiant Floor Heating
- Challenges and Considerations
- FAQs
- Conclusion and summery
How Radiant Floor Heating Works

Radiant floor heating operates on the principle of thermal radiation, where heat is transferred directly from a warm surface to cooler objects in the room, including people and where cost efficiency matters! This method contrasts with traditional forced-air systems, offering a more efficient and comfortable way to warm living spaces.
In a water-based Radiant floor heating system, a boiler or water heater heats water and circulates it through a network of pipes installed beneath the floor. The warmth from the circulating water gradually radiates upward, warming the floor surface. The floor, in turn, acts as a thermal mass, emitting heat to the surrounding space, creating a consistent and comfortable temperature. Look for maintenance tips for underfloor heating systems.
Electric Radiant floor heating systems utilize heating cables or mats installed directly beneath the flooring. These elements generate heat when an electric current passes through them, warming the floor surface. Electric systems are known for their quick response time and flexibility in zoned heating, allowing users to control specific areas of a building independently.
Both water-based and electric systems offer the advantage of even heat distribution, eliminating hot or cold spots commonly associated with forced-air systems. Like trace heating of pipe and vessel. The lower operating temperatures required for Radiant floor heating contribute to energy efficiency, making it a sustainable and cost-effective heating solution.
In summary, Radiant floor heating relies on the direct transfer of heat through floors, providing a silent, energy-efficient, and comfortable method of maintaining a warm indoor environment. Whether powered by water or electricity, this technology represents a modern and effective approach to heating homes and commercial spaces.
Advantages of Radiant Floor Heating
Radiant floor heating boasts several advantages that make it an increasingly popular choice for both residential and commercial applications. One key benefit lies in its efficiency. Unlike traditional forced-air systems that rely on convection to distribute heat, radiant systems directly transfer warmth from the floor to people and objects in the room. This results in a more uniform and comfortable temperature throughout the space.
Energy efficiency is another significant advantage. Radiant floor heating operates at lower temperatures compared to conventional systems, reducing heat loss and leading to potential energy savings. This efficiency is particularly notable in water-based systems where heated water circulates through pipes embedded in the floor, minimizing wasted energy.
Improved indoor air quality is a noteworthy advantage of Radiant floor heating. Without the need for ductwork, there is less circulation of dust, allergens, and other particles that can be associated with forced-air systems. Like LNG tanks and trace heating. This is particularly beneficial for individuals with respiratory issues or allergies.
The design flexibility offered by Radiant floor heating is also a notable advantage. With no need for radiators or visible vents, this system allows for more versatile and aesthetically pleasing interior designs. It is compatible with various flooring materials, from tile and stone to wood and carpet. Used in roofs and gutters.
In terms of comfort, Radiant floor heating provides a gentle and consistent warmth, eliminating cold spots and ensuring a cozy environment. Additionally, the lack of noisy fans or ductwork contributes to a quiet and peaceful atmosphere specially in open space heating and heating cable. In summary, the numerous advantages of Radiant floor heating make it a compelling choice for those seeking efficient, comfortable, and aesthetically pleasing heating solutions.
Types of Radiant Floor Heating Systems
Radiant floor heating systems come in various types, each offering unique features and advantages tailored to different needs and preferences. The two main categories are hydronic (water-based) and electric Radiant floor heating systems.
Hydronic underfloor heating systems utilize heated water to warm the floor. A boiler or water heater warms the water, which then circulates through a network of pipes installed beneath the floor. This type is known for its energy efficiency and compatibility with different flooring materials. Hydronic systems are further divided into wet and dry installations and loading and unloading process and heating cables. Wet installations involve embedding the pipes in a concrete slab, providing excellent thermal mass. Dry installations, on the other hand, involve placing the pipes in grooved panels above the subfloor, offering a more responsive heating solution.
Electric Radiant floor heating systems use electric cables or mats to generate heat directly beneath the flooring. These systems are known for their quick response time and suitability for smaller spaces or specific zones within a building. Electric systems are often used in retrofitting projects due to their ease of installation and compatibility with various floor coverings.
Within these categories, there are variations such as electric cable systems with self-adhesive mats for simple installation or hydronic systems with modular panels for efficient heat distribution. The choice between hydronic and electric systems depends on factors like energy source availability, cost considerations, and the specific heating requirements of the space. Similar to silo heating and heating cables. Overall, the diverse types of Radiant floor heating systems provide flexibility for users to select the most suitable option based on their preferences and practical considerations.
Installation Process and Considerations of radiant floor heating

The installation of Radiant floor heating involves careful planning and consideration of various factors to ensure optimal performance and efficiency. The process varies depending on whether it’s a hydronic (water-based) or electric system. What do you think about hydrogen process and heat-tracing ? Which one is it?
For hydronic systems, the installation typically begins with laying out the tubing within the subfloor or on top of it, depending on the chosen method (wet or dry installation). In wet installations, the tubing is embedded in a concrete slab, creating a thermal mass that stores and radiates heat, helping oil and gas industry and underfloor heating. Dry installations involve securing the tubing in grooved panels above the subfloor, allowing for a quicker response time. The tubing layout should account for the specific heating needs of different areas within the space.
Electric Radiant floor heating systems are often simpler to install. The electric cables or mats are placed directly beneath the flooring, either within thin-set mortar for tile and stone surfaces or self-adhesive mats for other flooring materials. This method is particularly suitable for retrofitting projects due to its minimal impact on floor height.
Considerations during installation include the selection of an appropriate heat source, whether a boiler for hydronic systems or an electrical power source for electric systems. Proper insulation beneath the heating elements is crucial to prevent heat loss. Additionally, zoning the system, especially in larger spaces, allows for more precise control and energy efficiency. Some interesting related product would be : underfloor heating straps.
Regardless of the system type, it’s essential to consult with professionals to ensure proper installation and adherence to local building codes. The careful consideration of factors such as insulation, zoning, and layout contributes to the successful implementation of Radiant floor heating, providing a comfortable and energy-efficient heating solution.
Costs and Return on Investment of radiant floor heating
The costs associated with installing Radiant floor heating systems vary based on factors such as system type, size of the area, and the chosen method of installation. Generally, hydronic (water-based) systems tend to have higher upfront costs due to the need for a boiler or water heater, as well as the intricate tubing installation. Electric systems, on the other hand, may have lower initial costs, making them more budget-friendly.
Hydronic systems often offer better long-term energy efficiency, potentially leading to lower operational costs over time. The efficiency of Radiant floor heating, in general, allows users to operate the system at lower temperatures than traditional heating methods, resulting in energy savings and associating with household underfloor heating.
Return on investment (ROI) for Radiant floor heating systems can be influenced by factors such as local energy costs, the duration the system is in use, and the insulation of the space. In climates with colder temperatures, where heating is required for more extended periods, the investment in Radiant floor heating becomes more appealing to industry and the underfloor heating systems due to consistent energy savings.
Additionally, the increased comfort and potential boost in property value are intangible returns that contribute to the overall appeal of Radiant floor heating. While the initial costs may be higher compared to conventional heating systems, the long-term benefits, both in terms of energy efficiency and comfort, can make Radiant floor heating a sound investment for homeowners and businesses seeking a reliable and effective heating solution. Consulting with professionals for a detailed cost analysis based on specific requirements is advisable for accurate budgeting and assessing the return on investment and staying away from hazard zones in the underfloor heating industry.
Maintenance Tips for Radiant floor Heating Systems
Maintaining radiant heating systems is essential for ensuring their longevity and optimal performance. Here are key tips to keep these systems running smoothly:
1. Regular Inspection: Periodically inspect the entire system, including pipes, tubing, and heating elements. Look for any signs of leaks, damage, or wear. Addressing issues promptly can prevent more significant problems down the line.
2. Check for Air Pockets (Hydronic Systems): In hydronic systems, air pockets can hinder proper water circulation. Bleed the system regularly to remove any trapped air, ensuring efficient heat transfer.
3. Clean Heating Elements for the health benefits of underfloor heating systems: For electric systems, ensure the heating cables or mats remain free from debris and dust. A clean surface allows for better heat conduction and prevents overheating.
4. Monitor Thermostats: Regularly check and calibrate thermostats to maintain accurate temperature control. Malfunctioning thermostats can lead to uneven Radiant floor heating or increased energy consumption.
5. Inspect Flooring: Keep an eye on the condition of the flooring above the radiant heating elements. If using carpet, ensure it does not impede heat transfer. For tile or stone, check for cracks or damage that could affect heat distribution.
6. Conduct Efficiency Checks: Periodically assess the energy efficiency of the system. Check for any decrease in heating performance or unexpected increases in energy consumption, as these could indicate underlying issues.
7. Professional Maintenance: Schedule professional maintenance at least once a year. Certified technicians can perform thorough inspections, identify potential problems, and conduct necessary repairs or adjustments and do the installation process of underfloor heating systems carefully.
8. Protect Pipes from Freezing (Hydronic Systems): In colder climates, take precautions to prevent freezing of water in hydronic systems. Proper insulation and anti-freeze solutions can safeguard against winter-related issues.
By incorporating these maintenance practices into a routine, users can ensure the longevity and reliable operation of their Radiant floor heating systems, making the ease and comfort of underfloor heating systems consistent and energy efficiency.
Environmental Impact of Radiant floor Heating
Radiant floor heating systems offer several environmental benefits, making them a sustainable choice for those seeking energy-efficient and eco-friendly heating solutions. One key advantage lies in their efficiency, as radiant systems operate at lower temperatures compared to traditional forced-air systems. This reduced operating temperature translates to lower energy consumption, contributing to overall energy conservation and upgrading the quality and long-term support of underfloor heating systems.
The even distribution of heat in radiant systems further enhances their environmental impact. By directly warming surfaces and objects, these systems minimize heat loss and improve the overall effectiveness of heating, leading to less wasted energy. Additionally, the ability to zone radiant heating systems allows users to heat specific areas only when needed, reducing energy usage and further lowering environmental impact. Like the technology uses in parallel silicone heating cable.
The choice of energy source also plays a role in the environmental footprint of radiant heating. Hydronic systems can utilize renewable energy sources such as solar or geothermal energy to heat the circulating water, aligning with sustainable practices. Electric systems, when powered by renewable energy, contribute to a cleaner energy mix.
Furthermore, radiant heating’s potential to enhance indoor air quality adds to its positive environmental profile improving underfloor heating systems. Without the need for ductwork, there is less circulation of allergens and pollutants, creating a healthier indoor environment.
In summary, the environmental impact of radiant heating systems is characterized by their energy efficiency, even heat distribution, zoning capabilities, and compatibility with renewable energy sources. By choosing Radiant floor heating, individuals contribute to a greener and more sustainable approach to indoor climate control.
Popular Applications of Radiant Floor Heating

Radiant floor heating has gained popularity across various applications due to its efficiency, comfort, and aesthetic advantages.
1. Residential Homes: This type of heating is widely used in residential properties, providing a luxurious and even warmth throughout the home. Can not ignore thermostats and their role in home heating It is compatible with various flooring materials, making it a versatile choice for bedrooms, living rooms, kitchens, and bathrooms.
2. Bathrooms: The comfort of stepping onto a warm floor in a bathroom is a common application of radiant heating. It not only enhances the comfort of the space but also helps in drying wet surfaces more quickly.
3. Commercial Buildings: This type of floor heating is increasingly being integrated into commercial spaces such as offices, hotels, and retail establishments. The silent and invisible heating method allows for flexibility in interior design without the need for bulky heating elements.
4. Greenhouses: In agricultural settings, Radiant floor heating is utilized in greenhouses to maintain optimal growing conditions for plants. The even distribution of heat helps in preventing frost and provides a controlled environment for plant cultivation. Related blog: home heating industry and the environment.
5. Hospitals and Healthcare Facilities: Radiant heating is employed in healthcare settings for its ability to create a comfortable and sterile environment. The absence of forced-air systems reduces the circulation of dust and allergens, contributing to improved indoor air quality.
6. Industrial Spaces: Large industrial facilities benefit from Radiant floor heating in specific zones where precise temperature control is crucial. Heat tracing cables come handy! This application ensures a comfortable working environment for employees while minimizing energy consumption.
7. Sports Arenas and Stadiums: This type of heating is used in arenas and stadiums, providing warmth to seating areas and ensuring the comfort of spectators during events.
Overall, the adaptability and efficiency of Radiant floor heating systems have made them a popular choice in diverse settings, offering a balance of comfort, energy efficiency, and aesthetic appeal.
Challenges and Considerations of radiant floor heating
While Radiant floor heating systems offer numerous advantages, there are also challenges and considerations that should be taken into account during the planning and installation phases.(New information about radiant floor heating)
1. Upfront Costs: The initial investment for Radiant floor heating systems, especially hydronic systems, can be higher than traditional heating systems. This cost includes the purchase and installation of boilers, tubing, or electric heating elements.
2. Installation Complexity: The installation process can be more complex, especially for hydronic systems that require embedding tubing in concrete or placing it in grooved panels. This complexity may lead to longer installation times and potentially higher labor costs. One good product would be: The best heating cable with inactive copper.
3. Retrofitting Challenges: Retrofitting existing structures with Radiant floor heating can be challenging, particularly in buildings with limited access to the subfloor. This can lead to increased installation costs and potential disruptions to the existing structure.
4. Response Time: While electric radiant systems have a quick response time, hydronic systems may take longer to warm up. This delay could be a consideration for those who require immediate or variable heating in specific areas. Using self-regulating heating cables.
5. Maintenance Access: If issues arise with the system, gaining access for repairs, especially in hydronic systems with embedded components, can be challenging. Proper planning and incorporating access points during installation can mitigate this challenge.
6. Compatibility with Flooring: Certain flooring materials may impact the efficiency of radiant heating. For example, thick insulating materials can impede heat transfer, affecting the system’s performance. Related product: the best underfloor heating film.
7. Zoning Considerations: Zoning the system is essential for energy efficiency and comfort, but improper zoning can lead to uneven heating or increased energy consumption. Careful consideration of the space’s layout and heating needs is crucial during the planning phase.
Addressing these challenges involves thorough planning, professional consultation, and consideration of factors such as the building’s structure, energy requirements, and the specific needs of the occupants. While Radiant floor heating provides numerous benefits, understanding and mitigating these challenges is crucial for a successful and efficient system implementation.
FAQs
Frequently Asked Questions About Radiant floor heating:
1. Q: How does Radiant floor heating work?
– A: Radiant floor heating works by circulating warm water through pipes or using electric heating elements beneath the floor. The heat then radiates upward, warming the room from the ground up.
2. Q: What are the main types of Radiant floor heating systems?
– A: There are two main types—hydronic (water-based) and electric. Hydronic systems use heated water in pipes, while electric systems use electric cables or mats directly beneath the flooring.
3. Q: Is Radiant floor heating energy-efficient?
– A: Yes, this type of heating heating is known for its energy efficiency. It operates at lower temperatures, reducing heat loss and potentially lowering energy consumption compared to traditional heating systems.
4. Q: Can Radiant floor heating be installed in existing homes?
– A: Yes, this type of floor heating can be retrofitted into existing homes. However, the complexity of installation may vary, and it’s advisable to consult with professionals for the best approach.
5. Q: Is Radiant floor heating compatible with all flooring types?
– A: Radiant heating is compatible with various flooring materials, including tile, stone, wood, and carpet. However, thick insulating materials may impact heat transfer.
6. Q: What is the lifespan of a Radiant floor heating system?
– A: With proper installation and maintenance, Radiant floor heating systems can have a lifespan of 25 years or more.*
7. Q: How does radiant heating impact indoor air quality?
– A: Radiant heating, by eliminating the need for ductwork, can contribute to better indoor air quality as it reduces the circulation of dust and allergens.
8. Q: Can Radiant floor heating be used for cooling as well?
– A: While primarily a heating system, some hydronic systems can be adapted for radiant cooling by circulating chilled water. However, it’s less common than radiant heating.
9. Q: Can I install Radiant floor heating in specific rooms or zones?
– A: Yes, this type of floor heating systems can be zoned, allowing for independent temperature control in different areas of the home or building.
10. Q: What are the maintenance requirements for Radiant floor heating?
– A: Regular inspection, cleaning, and professional maintenance are recommended. Tasks may include checking for leaks, ensuring proper insulation, and monitoring system efficiency.
conclusion

In conclusion, Radiant floor heating stands as a modern and innovative solution, offering a myriad of benefits that contribute to its increasing popularity in both residential and commercial settings. This heating method’s efficiency and ability to provide consistent warmth throughout a space make it a sought-after choice for those looking to enhance comfort while optimizing energy use in underfloor heating cables.
The even distribution of heat from the floor upwards not only ensures a cozy environment but also minimizes energy loss, marking a departure from the inefficiencies associated with traditional forced-air systems. This energy efficiency, coupled with the potential for lower operating temperatures, not only saves on utility costs but also aligns with the broader global emphasis on sustainable and eco-friendly practices.
Radiant floor heating is adaptable, accommodating various flooring materials and design preferences. Its compatibility with different surfaces, from tile and stone to wood and carpet, provides users with the flexibility to integrate this system seamlessly into diverse interior aesthetics. Related to constant wattage heating cable.
The improved indoor air quality is a noteworthy advantage, particularly for individuals with respiratory sensitivities. The absence of ductwork reduces the circulation of dust, allergens, and other airborne particles, contributing to a healthier living or working environment.
While Radiant floor heating may present initial installation costs and challenges, the long-term benefits in terms of energy efficiency, comfort, and design flexibility often outweigh these considerations. The lifespan of the system, when properly installed and maintained, adds to its appeal, making it a durable investment for those seeking a reliable and sustainable heating solution.
As the quest for efficiency and sustainability and environmentally conscious technologies continues, Radiant floor heating stands as a testament to the evolving landscape of climate control solutions, offering a warm embrace that extends beyond immediate comfort to encompass efficiency, sustainability, and a holistic approach to indoor well-being.







